Understanding Spina Bifida: A Brief Overview
Spina bifida is a congenital disorder that occurs when the spine and spinal cord don't develop properly during the early stages of pregnancy. This defect can result in nerve damage, physical disabilities, and various other complications. As a blogger and a concerned individual, I believe that it is essential to raise awareness about this condition and the significance of continued research and innovation in this field. In this article, I will discuss various aspects of spina bifida, its impact on affected individuals, and the importance of research and innovation in finding better treatments and preventive measures.
Causes and Risk Factors of Spina Bifida
Although the exact cause of spina bifida is still unknown, researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors play a role in its occurrence. Some of the known risk factors include a family history of neural tube defects, certain medications taken during pregnancy, and maternal diabetes. Additionally, inadequate intake of folic acid, a crucial nutrient for fetal development, has been linked to an increased risk of spina bifida. It's essential for pregnant women and those planning to conceive to be aware of these risk factors and take necessary precautions to minimize the chances of their unborn child developing this condition.
Types and Severity of Spina Bifida
Spina bifida can be classified into three main types, each with varying degrees of severity. The mildest form is spina bifida occulta, which often goes unnoticed as it doesn't cause any visible symptoms. The other two types, meningocele and myelomeningocele, are more severe and involve the protrusion of spinal cord tissues and membranes through an opening in the spine. Myelomeningocele, also known as open spina bifida, is the most severe form and can lead to significant neurological problems and physical disabilities. Understanding the different types and severity of this condition helps in better management of the affected individuals and paves the way for more targeted research and innovation.
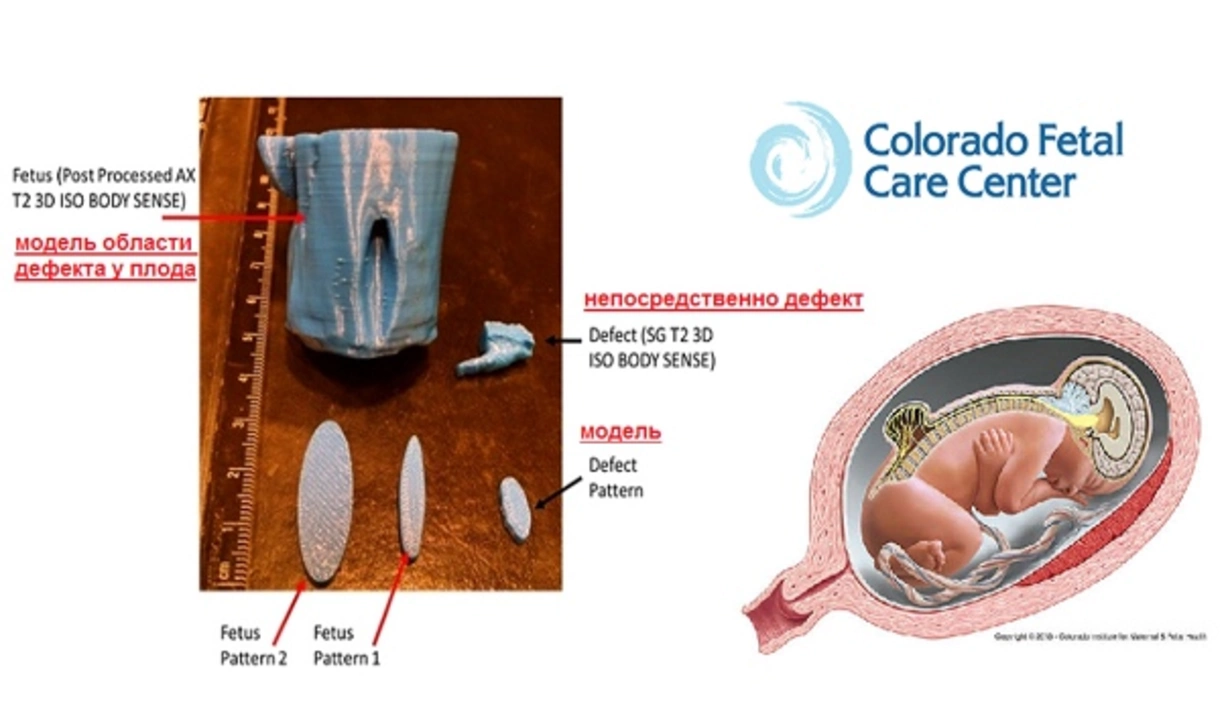
Diagnosis and Prenatal Screening
Spina bifida can often be diagnosed before birth through prenatal screening tests, such as blood tests and ultrasound examinations. These tests help detect the presence of certain markers or abnormalities indicative of spina bifida. In some cases, amniocentesis may also be performed to obtain a more accurate diagnosis. Early detection of spina bifida is crucial as it allows parents and healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding the management and treatment of the condition, and in some cases, opt for prenatal surgery to repair the defect.
Treatment and Management of Spina Bifida
Although there is no cure for spina bifida, various treatment options are available to manage the condition and improve the quality of life for affected individuals. Surgical interventions, either before or after birth, can help repair the spinal defect and prevent further complications. Children with spina bifida may also require ongoing medical care, physical therapy, and assistive devices to address mobility issues and other associated problems. Research and innovation play a critical role in finding new and improved treatment options that can significantly enhance the lives of those living with spina bifida.
Prevention and the Role of Folic Acid
Preventing spina bifida primarily involves the consumption of adequate amounts of folic acid before and during pregnancy. Folic acid is a B-vitamin that plays a vital role in the formation of the neural tube, and its deficiency can increase the risk of spina bifida and other neural tube defects. Women of childbearing age are advised to take folic acid supplements and consume a diet rich in natural food sources of this nutrient, such as leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, and fortified cereals. Public health campaigns and educational initiatives can help raise awareness about the importance of folic acid in preventing spina bifida and promote its consumption among women of reproductive age.
The Future of Spina Bifida Research and Innovation
Continued research and innovation in the field of spina bifida hold the key to better understanding this complex condition, finding more effective treatments, and discovering preventive measures. Ongoing studies focus on various aspects, such as the role of genetics, the development of new surgical techniques, and the potential benefits of stem cell therapy. By supporting and investing in spina bifida research, we can contribute to a brighter future for millions of affected individuals and their families, and ultimately, help reduce the global burden of this debilitating condition.


Kamal ALGhafri
May 5, 2023 AT 02:40Spina bifida exemplifies the ethical imperative for societies to allocate resources toward prenatal research, as neglecting such conditions undermines our collective responsibility to the most vulnerable.
Gulam Ahmed Khan
May 5, 2023 AT 21:16We're all in this together 😊! Supporting research not only advances science but also offers hope to families facing this challenge.
John and Maria Cristina Varano
May 6, 2023 AT 15:53Honestly this article is just another hype piece about folic acid and prenatal scans. The real issue is funding and bureaucracy, not some vague "research" buzzword.
Melissa Trebouhansingh
May 7, 2023 AT 10:30While I acknowledge the sentiment expressed by some contributors, one must recognize that the discourse surrounding congenital anomalies, such as spina bifida, is inextricably bound to a tapestry of interdisciplinary scholarship, public policy, and the ever‑evolving landscape of biomedical ethics. It is insufficient, therefore, to reduce this complex tableau to mere "research hype" without an appreciation for the nuanced interplay of genetics, maternal nutrition, and socioeconomic determinants that collectively shape incidence rates. Moreover, the historical context of folic acid fortification programs illustrates a seminal triumph of preventive medicine that warrants commendation rather than dismissal. By fostering a collaborative environment wherein clinicians, epidemiologists, and patient advocacy groups co‑author a shared vision, we incrementally transcend the limitations imposed by fragmented funding streams. Consequently, the pursuit of innovative therapeutic modalities-ranging from in‑utero surgical interventions to emergent stem‑cell therapies-should be heralded as a beacon of optimism for affected families. In sum, the narrative must evolve beyond reductive critiques and instead celebrate the synergistic potential inherent in a concerted, evidence‑based approach.
Brian Rice
May 8, 2023 AT 05:06It is incumbent upon us, as a civilized society, to confront the moral dimensions of spina bifida without succumbing to fatalistic resignation; the data unequivocally demonstrate that targeted nutritional supplementation and early diagnostic modalities yield tangible benefits for both patient and parent alike.
Stan Oud
May 8, 2023 AT 23:43While your moral framing is certainly lofty, let us not ignore the practical constraints-budgetary shortfalls, bureaucratic inertia, and the occasional over‑promising of "miracle cures" that never materialize.
Ryan Moodley
May 9, 2023 AT 18:20Contrary to popular belief, pouring more money into prenatal screening may simply shift the burden onto parents rather than solving the underlying genetic complexities of spina bifida.
carol messum
May 10, 2023 AT 12:56Every bit of awareness helps.
Jennifer Ramos
May 11, 2023 AT 07:33Great post! 🌟 I think spreading the word about folic acid and supporting research grants can make a real difference for families.
Grover Walters
May 12, 2023 AT 02:10Indeed, the collaborative effort between clinicians and policymakers is essential; however, we must also remain vigilant about the ethical considerations of prenatal interventions.
Amy Collins
May 12, 2023 AT 20:46From a biotech standpoint, leveraging CRISPR platforms could someday target the root cause, but we’re still in the hype phase.
amanda luize
May 13, 2023 AT 15:23Let me point out that mainstream narratives about "research progress" often conceal hidden agendas; the pharmaceutical lobby benefits from the perpetual uncertainty surrounding neural tube defects. One should question why certain data are withheld and why the so‑called "preventative" campaigns focus exclusively on folic acid while ignoring potential environmental toxins deliberately downplayed in corporate reports.
Chris Morgan
May 14, 2023 AT 10:00While the concerns raised are noted, dismissing decades of epidemiological evidence in favor of conspiracy undermines genuine scientific discourse.
Pallavi G
May 15, 2023 AT 04:36Happy to add some practical tips: ensure you’re getting 400‑800 µg of folic acid daily, consider a prenatal vitamin with added B‑vitamins, and schedule a detailed ultrasound by 18‑20 weeks to spot neural tube anomalies early.
Rafael Lopez
May 15, 2023 AT 23:13In addition to what has been said, I would recommend: • Consulting a genetics counselor if there is a family history; • Keeping a balanced diet rich in leafy greens; • Staying informed about emerging clinical trials that might offer novel therapeutic options.
Craig Mascarenhas
May 16, 2023 AT 17:50People keep saying "trust the science", but why are we never told about the hidden side‑effects of the substances used in prenatal surgeries? There’s a reason the data is scarce.
aarsha jayan
May 17, 2023 AT 12:26Let’s keep the conversation respectful and inclusive; sharing credible resources and personal experiences can empower others without resorting to fear‑mongering.
Rita Joseph
May 18, 2023 AT 07:03I’m curious about the latest stem‑cell research-has anyone seen recent peer‑reviewed results showing functional improvement in motor outcomes for spina bifida patients?