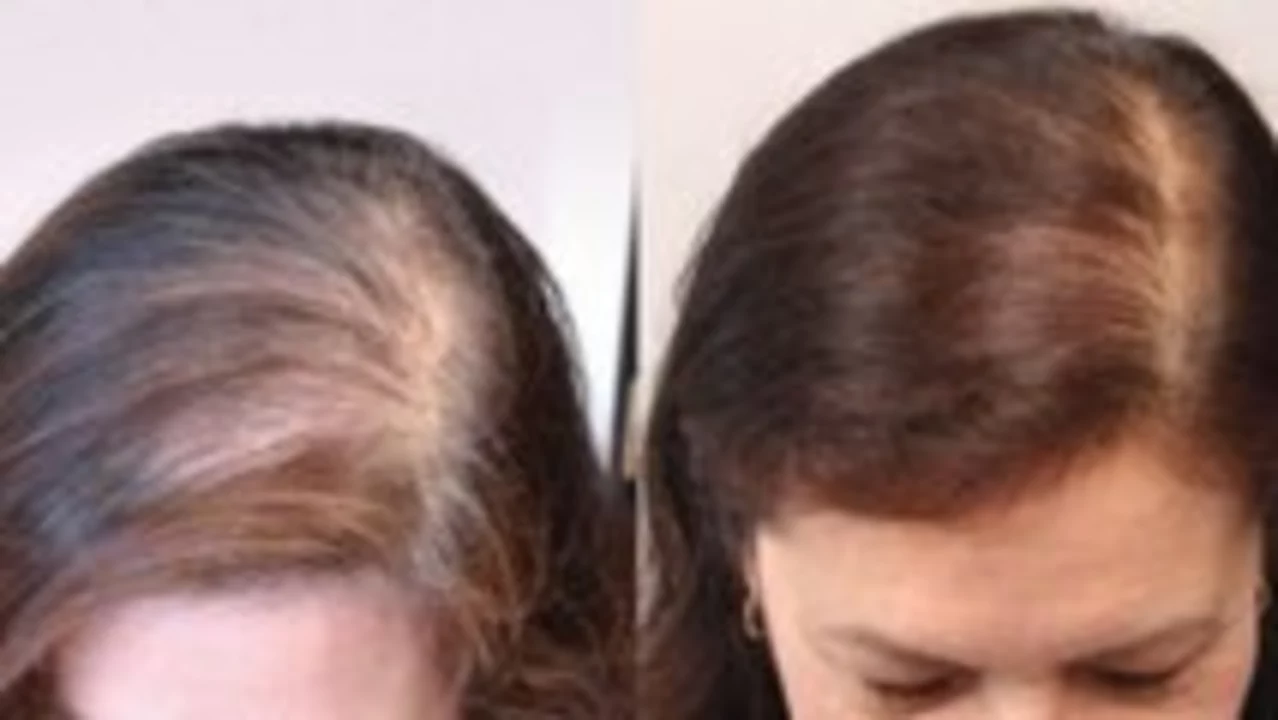
Hair loss: practical help, treatments and when to act
Hair loss can feel personal and sometimes sudden. This tag page groups straightforward articles, drug guides, and safe-buying tips so you can find answers fast. Whether you want to stop shedding, check a medicine’s side effects, or learn safe online pharmacy steps, you’ll get clear, usable advice here.
Most hair loss falls into a few simple categories: male or female pattern baldness, temporary shedding after stress or illness, medication-related loss, and autoimmune patchy hair loss. Genetics and hormones drive the common pattern types. Other causes like iron deficiency, thyroid problems, or certain drugs can trigger diffuse thinning. Spotting the pattern helps choose the right action.
Start with basic checks at home: compare photos from a year ago, note how much hair comes out when you brush, and check for scalp redness or scarring. Try improving routine factors first—eat protein, iron-rich foods, sleep more, and cut back on tight hairstyles. These steps won’t fix genetic baldness but often reduce unnecessary breakage and slow shedding.
Treatments that work
Topical minoxidil is the go-to over-the-counter option; it can thicken hair and slow loss if used consistently. For men, finasteride is an effective prescription pill that lowers DHT and can stop progression; it requires a doctor’s prescription and monitoring. Newer choices include low-level laser devices and PRP injections; both show benefit for some people but vary in cost and availability. If you’re considering surgery, hair transplant techniques now yield natural results for many candidates.
Always weigh benefits and side effects. For example, some medications used for other conditions can cause shedding; steroids and certain cancer drugs are notable culprits. Talk with a clinician before starting or stopping any prescribed drug. If you buy treatments online, verify the pharmacy’s credentials and confirm the product matches the active ingredient you need.
When to see a doctor
Book a visit if you notice sudden heavy shedding, bald patches, scalp pain, or hair loss that follows a new medication. Ask for basic blood tests—CBC, ferritin, TSH—and consider a dermatologist referral for a scalp exam or biopsy if the cause is unclear. Early assessment gives the best chance to stop progression or fix reversible causes.
This tag gathers practical posts on treatments, safe online pharmacies, and specific drug effects. Use the filters to find step-by-step guides, product reviews, and safety checklists. If you’re unsure about a treatment or an online seller, ask a professional—quick checks often prevent big mistakes.
Expect to see results slowly: topical or oral treatments usually take three to six months before you notice less shedding and up to a year for thicker growth. Stick to one plan for at least six months unless side effects appear. Use a mild shampoo, avoid daily hot styling, and pat hair dry instead of rubbing. If you use supplements, choose ones with clear labels and check for iron or vitamin D deficiencies first. Track progress with photos every month so you can tell if a treatment is helping.
Ask early.