Understanding Torsemide and Hyperuricemia
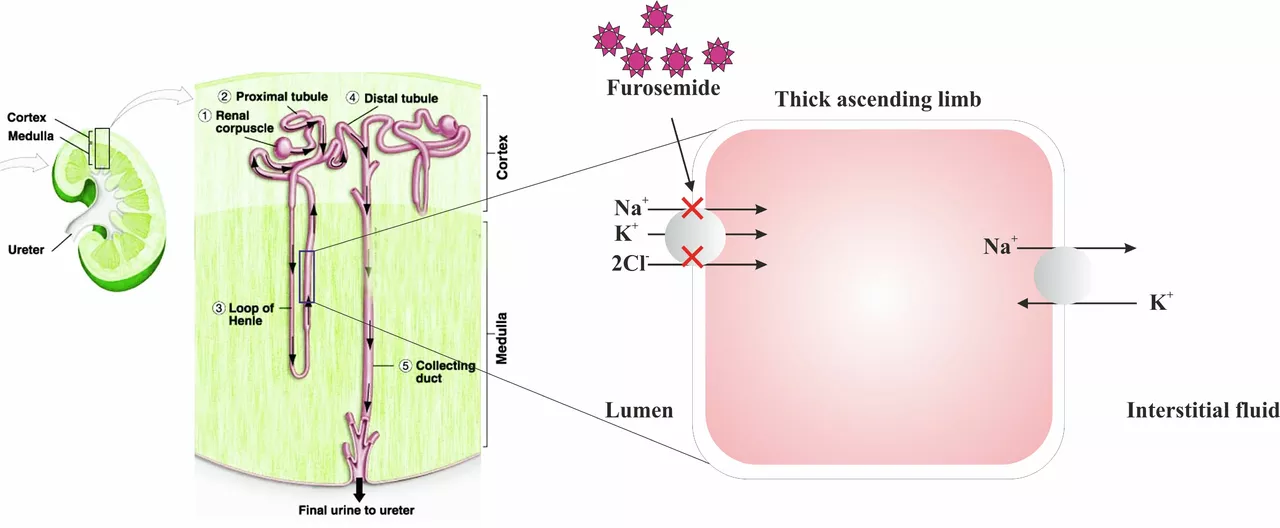
Before we delve into the connection between torsemide and hyperuricemia, it's essential to first understand what these two terms mean. Torsemide is a diuretic medication that is mainly used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and edema. It works by increasing the amount of urine produced by the kidneys, which helps in eliminating excess fluids and sodium from the body. Hyperuricemia, on the other hand, is a condition characterized by abnormally high levels of uric acid in the blood. This can lead to a variety of health issues, including gout and kidney stones.
How Torsemide Affects Uric Acid Levels
Now that we have a basic understanding of torsemide and hyperuricemia, let's look at how the medication can affect uric acid levels in the body. As a diuretic, torsemide increases the volume of urine produced by the kidneys. This increased urine production can cause uric acid to be excreted more rapidly, leading to a decrease in blood uric acid levels. However, in some cases, torsemide can also cause the kidneys to reabsorb more uric acid, which can result in an increase in blood uric acid levels and potentially contribute to hyperuricemia.
Torsemide-Induced Hyperuricemia: What the Research Shows
Several studies have examined the association between torsemide use and the development of hyperuricemia. In general, the findings suggest that while torsemide can lower blood uric acid levels in some individuals, it may also increase the risk of hyperuricemia in others. The exact reasons for this discrepancy are not yet fully understood, but it is believed that factors such as the individual's baseline uric acid levels, kidney function, and the presence of other health conditions may play a role in determining the medication's effect on uric acid levels.
Managing Hyperuricemia in Patients Taking Torsemide
If you or a loved one has been prescribed torsemide and are experiencing hyperuricemia, it's important to discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider. They may consider adjusting the dosage of the medication, switching to a different diuretic, or prescribing additional medications to help manage your uric acid levels. Additionally, making certain lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying well-hydrated, and avoiding foods high in purines, can also help in managing hyperuricemia.
Preventing Hyperuricemia in Patients at Risk
For patients who are at risk of developing hyperuricemia, it's crucial to take proactive measures to prevent the condition from occurring. This may include closely monitoring your blood uric acid levels, discussing any concerns with your healthcare provider, and making appropriate lifestyle changes. When prescribing torsemide, doctors should also be mindful of the potential risk of hyperuricemia, particularly in patients who have a history of gout or kidney stones, and consider alternative treatment options if necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while torsemide can be an effective treatment for high blood pressure, heart failure, and edema, it's important to be aware of the potential connection between the medication and hyperuricemia. By staying informed and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can better manage your uric acid levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with hyperuricemia. Remember, it's always better to be proactive and take steps to prevent potential health issues rather than addressing them once they've already developed.

darren coen
June 2, 2023 AT 19:31Hope this helps anyone dealing with torsemide and uric acid spikes.
Jennifer Boyd
June 8, 2023 AT 19:31If you’re on torsemide and spotting those uric acid swings, remember you’re not alone. I’ve seen patients turn their worries into triumphs by staying hydrated and tweaking their diet. The key is to keep the conversation open with your doc-don’t let the numbers scare you away. Your body can adapt, and with a few lifestyle tweaks you’ll feel like a champion again. Keep the vibe positive, and the results will follow!
Lauren DiSabato
June 14, 2023 AT 19:31One must acknowledge that the literature on torsemide’s impact on uricemia is replete with methodological inconsistencies. The prevailing hypothesis that loop diuretics uniformly lower uric acid is, frankly, a simplification worthy of a freshman lecture. Moreover, the author’s reliance on small cohort studies betrays a lack of rigorous statistical power. It would be prudent for clinicians to scrutinize the dosage–response relationship before promulgating blanket recommendations. In short, the discourse is far from settled, and the current article merely scratches the surface.
Hutchins Harbin
June 20, 2023 AT 19:31Interesting how the renal handling of uric acid shifts with varying loop diuretic doses. Data suggest a biphasic response-initially enhanced excretion followed by possible reabsorption at higher concentrations. This aligns with the mechanistic studies on Na‑K‑2Cl cotransporter inhibition. Clinicians should monitor serum uric acid periodically when titrating torsemide. Such vigilance can preempt gout flares and preserve kidney function.
Benjamin Herod
June 26, 2023 AT 19:31Ah, the tragic opera of medicine-where a drug meant to relieve fluid overload becomes the villain of gout. The patient, once hopeful, now watches crystal‑laden pain descend like a curtain call. Yet, let us not forget the noble intent behind torsemide’s prescription. It is a bittersweet symphony, dear reader, where balance is the only encore worth achieving.
luemba leonardo brás kali
July 2, 2023 AT 19:31Patient education is paramount. Explain the mechanism of torsemide and its potential effects on uric acid. Encourage regular blood tests. Discuss dietary purine intake. Recommend adequate hydration. This structured approach can mitigate hyperuricemia risk.
Corey McGhie
July 8, 2023 AT 19:31Your upbeat take is refreshing, but a reality check on lab monitoring keeps the optimism grounded.
Ajayi samson
July 14, 2023 AT 19:31Honestly, that pretentious whine about studies is just noise; the data clearly show torsemide can jack up uric acid for many patients, so stop pretending it’s a miracle.
Lief Larson
July 20, 2023 AT 19:31torsemide can be a double edged sword keep an eye on uric levels stay hydrated
Julia Grace
July 26, 2023 AT 19:31Yo! If uric acid’s actin' up, sprinkle some water, ditch the pizza and you'll be feelin' groovy!
Sadie Bell
August 1, 2023 AT 19:31Staying hydrated might help, just a thought.
Noah Bentley
August 7, 2023 AT 19:31There’s a typo in the phrase “hyperuricemia” – it’s spelled correctly here, but the article says “hyperuricemia”. Also, “diuretic” should not be capitalized.
Kathryn Jabek
August 13, 2023 AT 19:31The interplay between pharmacology and metabolic regulation invites a profound contemplation of bodily homeostasis.
When a patient consumes torsemide, the drug exerts its natriuretic influence, yet this very action may perturb the delicate balance of purine metabolism.
Hyperuricemia, as a manifestation of elevated serum uric acid, reflects both renal excretory capacity and intracellular production rates.
Scientific investigations have yielded heterogeneous findings, some indicating a reduction in uric acid due to increased diuresis, others revealing an unexpected rise associated with renal reabsorption mechanisms.
Such dichotomy underscores the necessity for individualized therapeutic assessment.
Clinicians ought to consider baseline uric acid levels, concomitant renal insufficiency, and the presence of comorbid gout when prescribing torsemide.
Moreover, the dose‑response relationship remains an area of incomplete knowledge, with higher doses potentially favoring reabsorption pathways.
Patients with pre‑existing hyperuricemia may experience exacerbation, thereby precipitating painful gout attacks.
Preventative strategies, including dietary purine restriction and adequate hydration, serve as adjunctive measures to pharmacologic control.
Regular monitoring of serum uric acid provides an empirical basis for therapeutic adjustments.
Should elevations persist, clinicians might contemplate alternative loop diuretics such as furosemide, which possess a distinct metabolic profile.
In addition, urate‑lowering agents like allopurinol can be co‑prescribed when the risk outweighs potential side effects.
From an ethical standpoint, informed consent must encompass a discussion of these metabolic risks, fostering patient autonomy.
The physician’s fiduciary duty extends beyond blood pressure normalization to encompass the holistic preservation of metabolic health.
In summary, torsemide’s impact on uric acid is neither uniformly beneficial nor uniformly deleterious; it occupies a nuanced middle ground.
A vigilant, patient‑centered approach remains the optimal pathway to harmonize therapeutic efficacy with metabolic safety.
Ogah John
August 19, 2023 AT 19:31Your philosophical tirade is impressive, yet the practical takeaway is simple: keep an eye on labs and adjust therapy before gout decides to crash the party.
Kelvin Murigi
August 25, 2023 AT 19:31Bottom line: stay proactive, track your uric acid, and work with your doctor to tailor torsemide use – that’s the safest route.